| Background | - Therapeutic class: Antipsychotic
- Pharmacologic class: Quinolinone derivatives
- Initial US approval: 2002
- Molecular Formula: C23H27Cl2N3O2
- Molecular weight: 448.38 g/mol
|
| Indications & Dosage | - Schizophrenia, bipolar mania, adjunctive treatment of major depressive disorder, irritability associated with autistic disorder, Tourette disorder
- Tablets: 2 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg
- Suspension (IM, extended release): 300 mg, 400 mg
- Oral solution: 1 mg/mL
|
| Pharmacokinetics | - Oral bioavailability: 87%
- Time to peak via oral route: 3-5 h
- Time to peak for intra-muscular route: 1-3 h; 4-7 days (Abilify Maintena)
- Peak plasma concentrations: 3–5 h
- Vd: 4.9 L/kg following IV administration
- Serum protein (mainly albumin) binding: >99%
- Pathways: dehydrogenation and hydroxylation by CYP2D6 and CYP3A4, N-dealkylation (CYP3A4)
- Major metabolite- dehydro-aripiprazole (40% of parent) is active
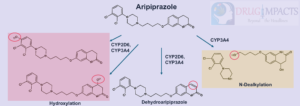
- The concentration ratios between the parent and metabolite is highly variable between patients with a mean of 40% (Kirschbaum et al., 2008)
- Elimination, half-life: 75 h for aripiprazole and 94 h for dehydro-aripiprazole
- Steady state attained within 14 days
- <1% unchanged in urine and ~18% unchanged in feces
|
| Mechanism of Action | - Partial dopamine D2 and serotonin 5-HT1A receptor agonist
- Serotonin 5-HT2A receptor antagonist
- Moderate affinity at dopamine D4, serotonin 5-HT2C and 5-HT7, alpha1-adrenergic and histamine H1 receptors
- Moderate affinity at serotonin reuptake receptor
|
| Adverse Effects | - Headache, asthenia, fever, nausea, vomiting, constipation, anxiety, insomnia, lightheadedness, somnolence, akathisia, blurred vision
- Nervous system: depression, nervousness, hostility, suicidal thought, manic reaction, abnormal gait, confusion, impaired concentration, impaired memory, stupor, slowed thinking
|
| Human Performance | Warning: May have the potential to impair judgment, thinking, and motor skills. Patients should be cautioned about operating hazardous machinery, including automobiles, until they know how it affects them.
- In a study of 28 schizophrenia patients where the median dose was 15 mg, 75% passed cognitive performance tests related to driving, which included visual perception, attention, working memory, and reaction time (Noh et al., 2020). This study has limitations in its design: for example, use of controls, statistical power, and patients taking other medications.
Therapeutic Concentrations:
- In a clinical study where 283 patients were given 7.5–60 mg/day and blood collected at least 12 h after the last dose, serum concentrations were as follows: aripiprazole mean = 0.214 mg/L; 25th – 75th range = 0.124 – 0.286 mg/L; dehydroaripiprazole mean = 0.078 mg/L, 25th – 75th range = 0.039 – 0.097 mg/L (Kirschbaum et al., 2008).
- High Performance Liquid Chromatography—UV detection was the choice of instrumentation with a validated analytical range of 0.05–1.00 mg/L.
- Another study showed that a 20 mg/day dose could reach concentrations of 0.270 mg/L, but Hart et al. (2022) suggested a therapeutic range for aripirazole: 0.12–0.27 mg/L and dehydroaripiprazole of 0.18–0.38 mg/L.
|
| Drug Interactions | - Avoid alcohol while taking Abilify. May increase CNS depression.
- Drugs that cause CNS depression such as benzodiazepines may increase CNS depression.
- Carbamazepine, a CYP3A4 inducer, when combined with Abilify, resulted in a 70% decrease in aripiprazole and its major metabolite, dehydro-aripiprazole.
|
| Further Reading | - Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Abilify (aripiprazole) [package insert]. U.S. Food and Drug Administration website. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2014/021436s038,021713s030,021729s022,021866s023lbl.pdf. Revised December 2014. Accessed February 20, 2024
- Kirschbaum, K. M., Müller, M. J., Malevani, J., Mobascher, A., Burchardt, C., Piel, M., & Hiemke, C. (2008). Serum levels of aripiprazole and dehydroaripiprazole, clinical response and side effects. The World Journal of Biological Psychiatry, 9(3), 212-218.
- Hart, X. M., Hiemke, C., Eichentopf, L., Lense, X. M., Clement, H. W., Conca, A., … & Gründer, G. (2022). Therapeutic reference range for aripiprazole in schizophrenia revised: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Psychopharmacology, 239(11), 3377-3391.
- Noh, S., Na, E., Park, S. J., Kim, S. H., Evins, A. E., & Roh, S. (2020). Effects of various antipsychotics on driving-related cognitive performance in adults with schizophrenia. Journal of psychiatric research, 131, 152-159.
|